
It can increase or decrease your internal organs functionality, it can even affect your facial expressions, i.e. When the central nervous system becomes damaged or peripheral nerves become trapped, a variety of impacts are possible. Together with the peripheral nervous system (PNS), it has a fundamental role in the control of behavior. The central nervous system (CNS) represents the largest part of the nervous system, including the brain and the spinal cord. The two systems function together, by way of nerves from the PNS entering and becoming part of the CNS, and vice versa.

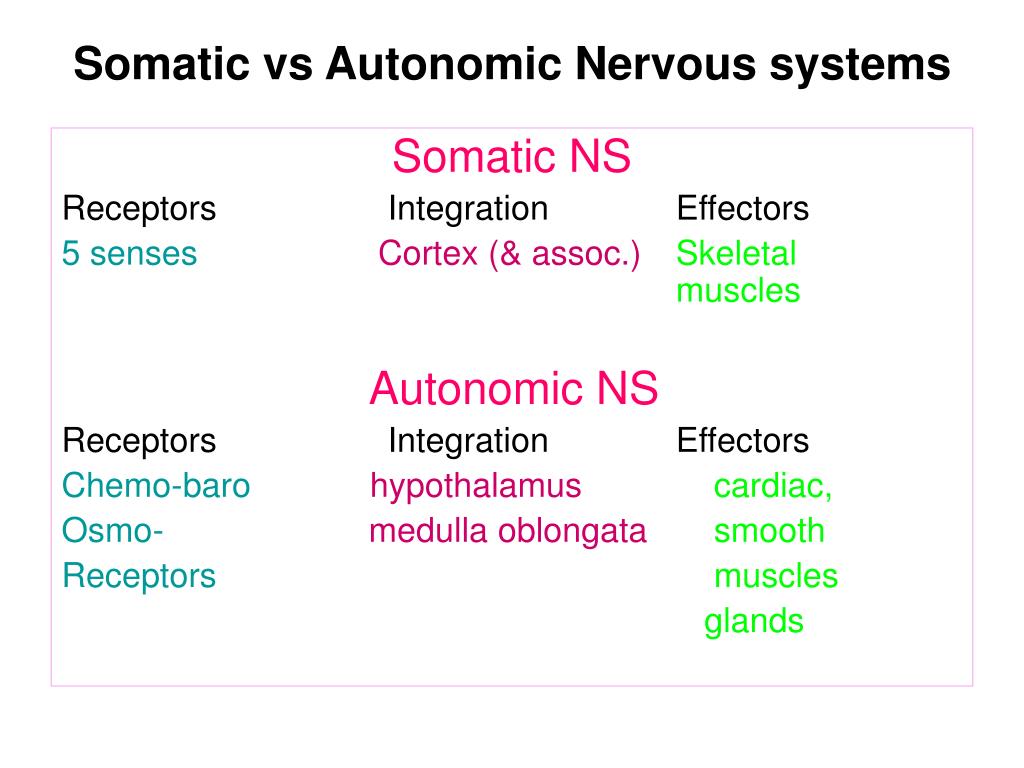
The somatic has voluntary control of skin, bones, joints, and skeletal muscle. The autonomic has involuntary control of internal organs, blood vessels, smooth and cardiac muscles. The PNS is then subdivided into the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. This information is sent to the CNS via afferent sensory nerves. It contains sensory receptors which help in processing changes in the internal and external environment. The PNS is a vast network of spinal and cranial nerves that are linked to the brain and the spinal cord. These centers can be subdivided to Lower Centers (including the spinal cord and brain stem) and Higher centers communicating with the brain via effectors. The brain is the body’s “control center.” The CNS has various centers located within it that carry out the sensory, motor and integration of data.
The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. The nervous system is comprised of two major parts, or subdivisions, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glia cells are found within tissues and are not excitable but help with myelination, ionic regulation and extracellular fluid. After the brain has processed the information, impulses are then conducted from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands, which is called motor output. The data is then processed by way of integration of data, which occurs only in the brain. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition, and although nerve cells can vary in size and location, their communication with one another determines their function. The nervous system is composed of excitable nerve cells (neurons) and synapses that form between the neurons and connect them to centers throughout the body or to other neurons.

Sensory input is when the body gathers information or data, by way of neurons, glia and synapses. The nervous system has three main functions: sensory input, integration of data and motor output.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
